Climate Change: All You Need to Know

Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time. It refers to long-term shifts in temperature patterns and weather conditions on a global scale. This article aims to explore the causes, effects, and consequences of climate change, as well as mitigation strategies, adaptation measures, and individual actions that can help address this critical challenge.
Causes of Climate Change
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
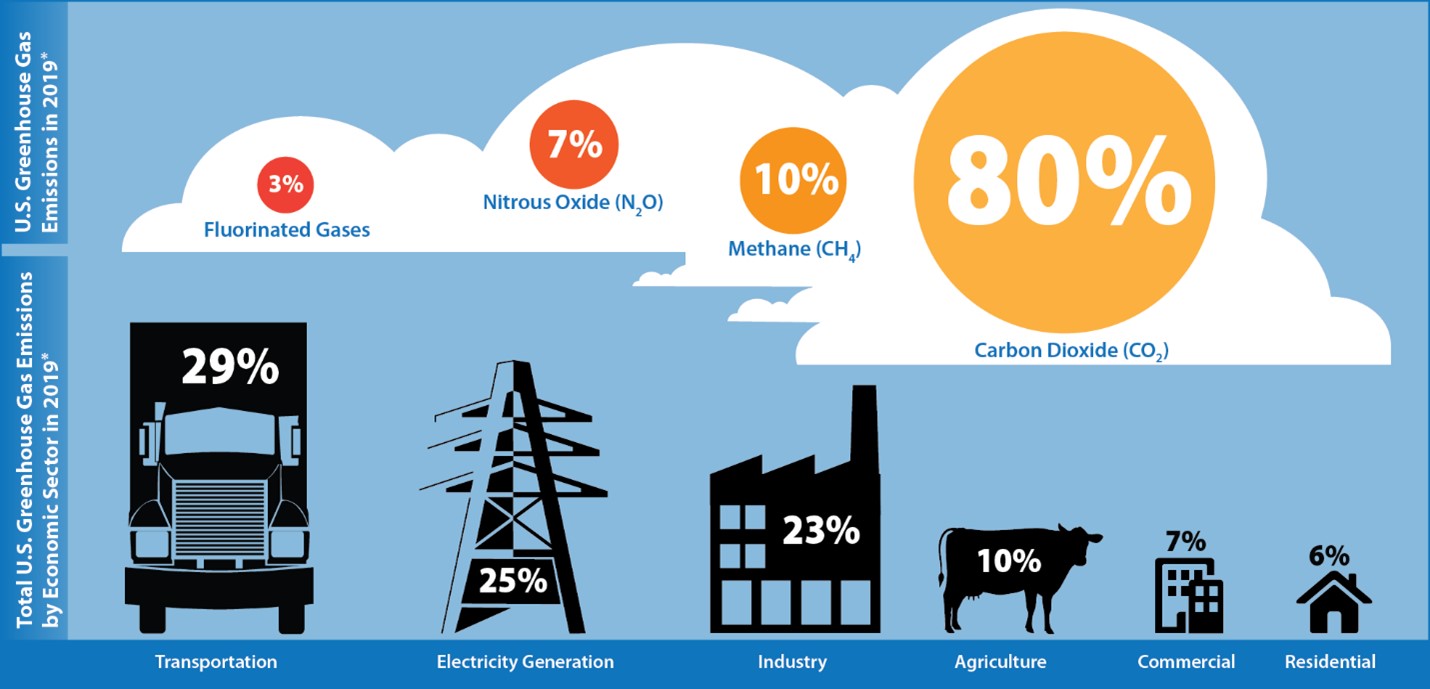
The primary cause of climate change is the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), released into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun, leading to a phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect. Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels for energy production, industrial processes, and transportation, contribute significantly to these emissions.
Deforestation
Deforestation also plays a significant role in climate change. Trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and act as carbon sinks. However, widespread deforestation, especially in tropical rainforests, reduces the Earth’s capacity to absorb CO2, resulting in higher concentrations of greenhouse gases.
Industrial Activities
Industrial activities, including manufacturing, mining, and chemical production, emit various greenhouse gases and pollutants into the atmosphere. These emissions contribute to air pollution, smog formation, and the intensification of climate change.
Effects of Climate Change
Rising Temperatures

One of the most evident effects of climate change is the rise in global temperatures. Over the past century, the Earth’s average temperature has increased, leading to warmer oceans, melting ice caps and glaciers, and the loss of permafrost. This temperature rise disrupts ecosystems and poses significant risks to human societies.
Extreme Weather Events
Climate change also contributes to an increase in extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heat waves. These events can have devastating impacts on communities, resulting in property damage, loss of lives, and economic disruptions.
Sea-level Rise
The melting of ice caps and glaciers, combined with the expansion of seawater due to higher temperatures, leads to sea-level rise. This phenomenon poses a significant threat to coastal areas, increasing the risk of flooding, erosion, and the loss of valuable ecosystems.
Impacts on Ecosystems
Loss of Biodiversity
Climate change poses a severe threat to biodiversity worldwide. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns disrupt ecosystems, leading to habitat loss, shifts in species distribution, and, in some cases, extinction. Protecting biodiversity is crucial for maintaining the overall health and functioning of ecosystems.
Disruption of Food Chains
Climate change can disrupt food chains and ecological interactions. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns affect the availability of food sources for various organisms, leading to imbalances in ecosystems. This disruption can have cascading effects on other species and ultimately impact human food security.
Coral Bleaching
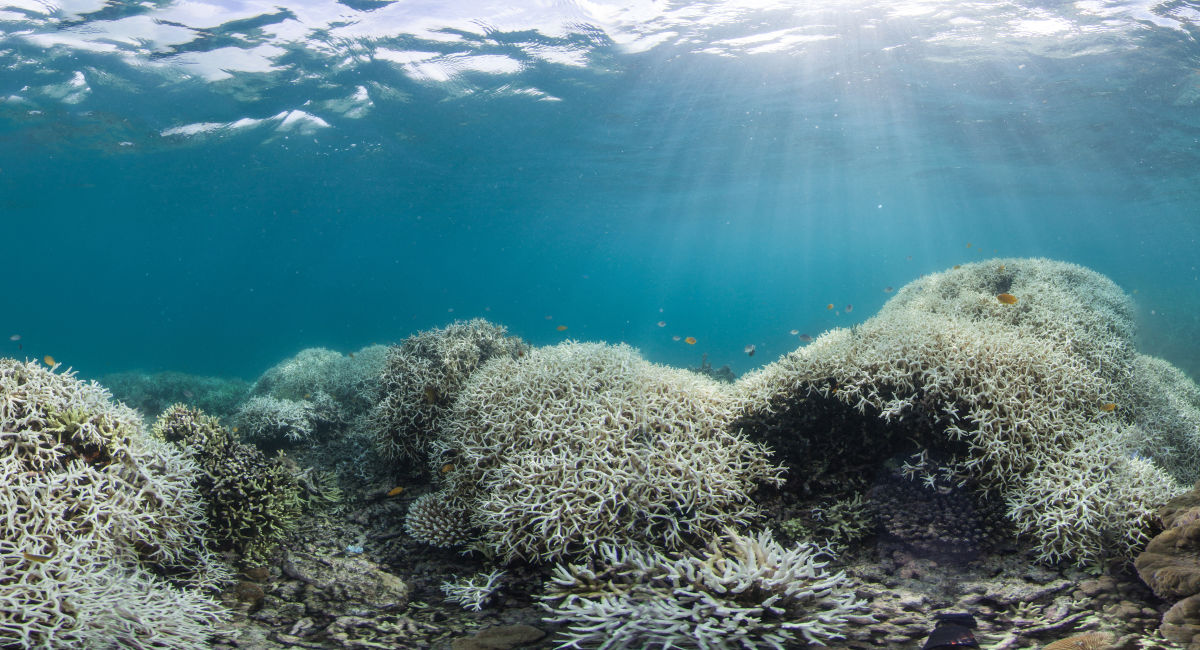

Rising ocean temperatures and increased acidification due to climate change contribute to coral bleaching. Corals, which are vital marine ecosystems, become stressed and lose their vibrant colors, making them more susceptible to disease and death. Coral bleaching has severe implications for marine biodiversity and coastal communities that rely on coral reefs for tourism and fisheries.
Human Health Consequences
Increased Heat-related Illnesses
As temperatures rise, the risk of heat-related illnesses, such as heatstroke and dehydration, increases. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are particularly at risk. Heatwaves can also exacerbate air pollution and respiratory issues.
Spread of Diseases
Climate change influences the geographic distribution of diseases. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can facilitate the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease. Changing ecosystems may also contribute to the emergence of new infectious diseases.
Mental Health Impacts
The psychological impacts of climate change are often overlooked but significant. Extreme weather events, displacement, and the loss of livelihoods can lead to stress, anxiety, and depression. It is crucial to address mental health concerns associated with climate change and provide support to affected communities.
Mitigation Strategies
Addressing climate change requires collective action and the implementation of various mitigation strategies. Here are some key approaches:
Transition to Renewable Energy
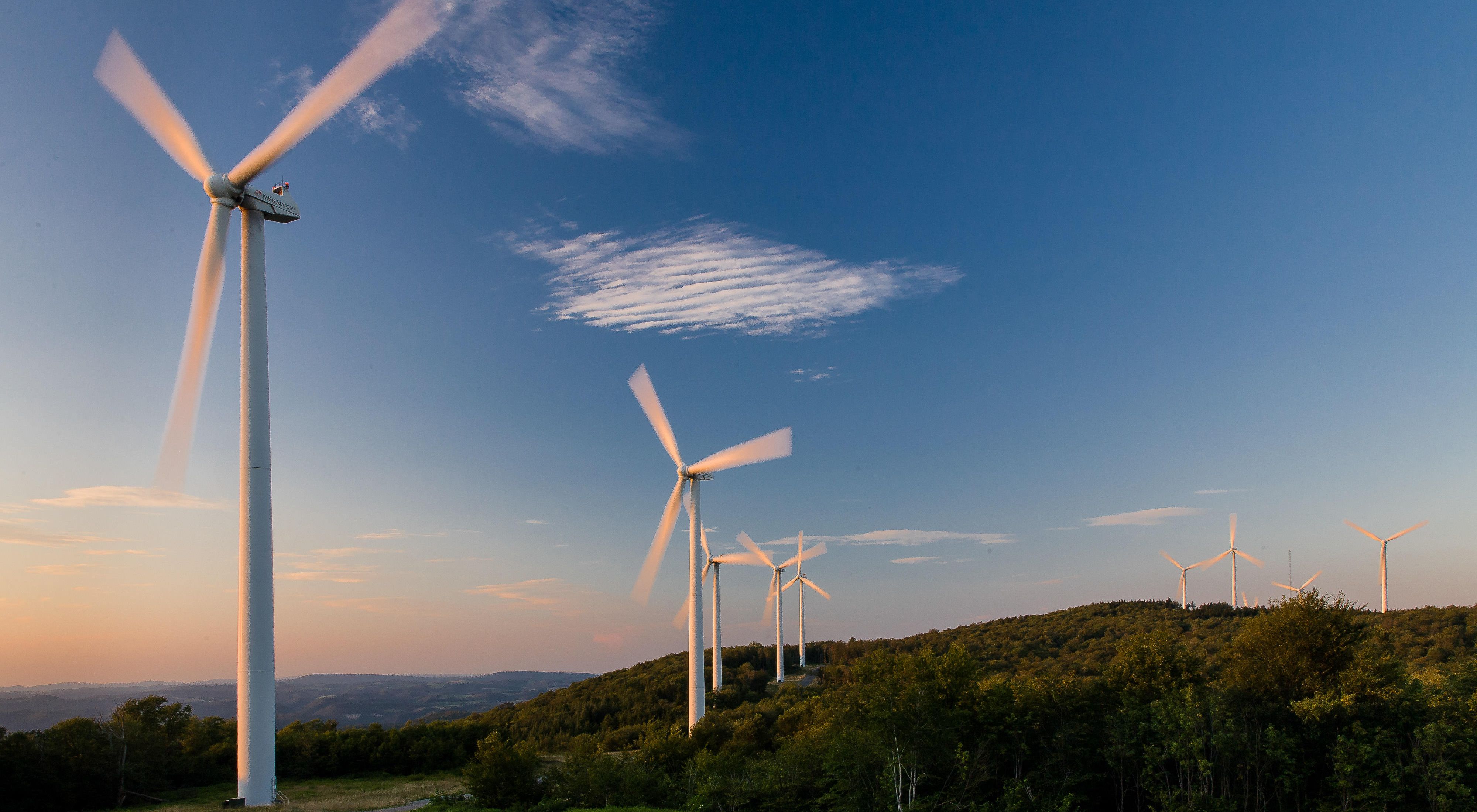

Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Governments, businesses, and individuals can promote renewable energy investments, improve energy efficiency, and adopt sustainable practices.
Sustainable Transportation
Transportation is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Encouraging the use of electric vehicles, promoting public transportation, and investing in infrastructure for walking and cycling can help reduce emissions and foster sustainable mobility.
Afforestation and Reforestation
Planting trees and restoring forest ecosystems can help sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Afforestation and reforestation initiatives play a vital role in mitigating climate change, enhancing biodiversity, and preserving essential habitats.
Adaptation Measures
In addition to mitigation, it is crucial to implement adaptation measures to address the impacts of climate change. Some key strategies include:
Building Resilient Infrastructure
Designing infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events and sea-level rise is essential for minimizing the potential damage and ensuring the safety of communities. This includes constructing flood-resistant buildings, improving drainage systems, and implementing early warning systems.
Enhancing Agricultural Practices
Climate change affects agriculture and food production. Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, such as precision farming, efficient water management, and the use of climate-resistant crop varieties, can help build resilience and ensure food security in a changing climate.
Implementing Water Management Strategies
Water scarcity and extreme precipitation events are anticipated consequences of climate change. Implementing water management strategies, such as rainwater harvesting, wastewater recycling, and efficient irrigation systems, can help ensure sustainable water use and reduce vulnerabilities.
International Efforts
Addressing climate change requires international cooperation and collective efforts. Key initiatives include:
The Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, is an international treaty aimed at limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. It outlines the commitments of nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance adaptation efforts, and provide financial support to developing countries.
COP28 Climate Change Conference
COP28 is the 28th Conference of Parties and will be held in 2023. It is a crucial international event where global leaders come together to discuss climate change and its impact on our planet. The conference is organized by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and is attended by representatives from over 190 countries. The conference is an opportunity for countries to share their progress towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and to work towards a more sustainable future.
Global Initiatives to Reduce Emissions
Various global initiatives and agreements focus on reducing emissions, promoting clean energy, and supporting sustainable development. Examples include the Clean Development Mechanism, the Kyoto Protocol, and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the United Nations and the World Bank, play a crucial role in facilitating collaboration, providing technical assistance, and mobilizing financial resources to address climate change. These organizations support research, policy development, and capacity-building efforts globally.
Individual Actions
While collective action is necessary, individual actions also contribute to addressing climate change. Here are some steps individuals can take:
Energy Conservation
Reducing energy consumption in daily activities, such as using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when not in use, and optimizing home heating and cooling systems, can help conserve energy and reduce carbon emissions.
Waste Reduction
Practicing waste reduction and recycling habits can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This includes minimizing single-use plastics, composting organic waste, and supporting recycling programs in communities.
Sustainable Consumption Habits
Making conscious choices in daily consumption, such as opting for sustainable products, supporting local and eco-friendly businesses, and reducing meat consumption, can contribute to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Climate change poses significant risks to our planet, environment, and society. It is essential to understand the causes, effects, and consequences of climate change, as well as take proactive measures to mitigate and adapt to its impacts. By implementing sustainable practices, supporting international efforts, and making individual choices, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.
FAQs
1. What is climate change?
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperature patterns and weather conditions on a global scale. It is primarily caused by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions and subsequent impacts on the environment.
2. How does climate change affect ecosystems?
Climate change disrupts ecosystems by causing habitat loss, shifts in species distribution, and increased vulnerability to extinction. It can also disrupt food chains, impact biodiversity, and lead to the loss of valuable ecosystems like coral reefs and rainforests.
3. What are the health consequences of climate change?
Climate change contributes to increased heat-related illnesses, the spread of diseases, and mental health impacts. Rising temperatures can lead to heatstroke and dehydration, while changes in ecosystems facilitate the spread of diseases like malaria. Additionally, extreme weather events and displacement can negatively impact mental health.
4. What can individuals do to address climate change?
Individuals can contribute to addressing climate change by conserving energy, reducing waste, and adopting sustainable consumption habits. Making choices such as using energy-efficient appliances, practicing recycling, and supporting local and eco-friendly businesses can make a positive impact.
5. How important is international cooperation in addressing climate change?
International cooperation is crucial in addressing climate change as it requires collective efforts and collaboration. Global agreements like the Paris Agreement and initiatives by international organizations facilitate coordination, support research and policy development, and mobilize resources to mitigate and adapt to climate change.




