Green Cities: Creating Sustainable and Livable Urban Environments

Green cities are a concept gaining momentum in the modern world as societies strive to build sustainable and livable urban environments. With the increasing urbanization and its associated challenges, it has become crucial to adopt eco-friendly practices that promote environmental preservation, enhance the well-being of residents, and drive economic growth. In this article, we will explore the concept of green cities, their benefits, key features, examples, challenges, solutions, the role of technology, and how they contribute to a better future for all.
What are Green Cities?
Green cities, also known as eco-cities or sustainable cities, are urban areas designed and developed with a focus on minimizing their environmental impact while improving the quality of life for residents. These cities prioritize sustainable practices across various sectors, including transportation, energy, waste management, and infrastructure. The aim is to create harmonious and balanced ecosystems where human activities coexist with nature in a mutually beneficial way.
Benefits of Green Cities
Environmental Benefits

One of the primary advantages of green cities is their positive impact on the environment. By implementing sustainable practices, these cities reduce greenhouse gas emissions, minimize pollution, and preserve natural resources. Green spaces, such as parks and urban forests, help mitigate the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and provide habitats for wildlife. Additionally, green cities promote biodiversity conservation, protecting and preserving ecosystems for future generations.
Health Benefits
Green cities prioritize the well-being of their residents by creating healthier living environments. By reducing pollution and improving air quality, they contribute to lower rates of respiratory diseases and allergies. Access to green spaces and recreational areas encourages physical activity, promoting better cardiovascular health and reducing stress levels. Furthermore, green infrastructure, such as green roofs and rain gardens, helps manage stormwater and mitigate the risk of flooding, safeguarding communities from natural disasters.
Economic Benefits
Contrary to popular belief, green cities can also be economically advantageous. By investing in renewable energy sources and energy-efficient buildings, cities can reduce their energy consumption and lower energy costs. Sustainable transportation systems, such as bike lanes and public transit networks, can reduce traffic congestion and improve productivity. Additionally, green cities attract businesses and investment, positioning themselves as innovative and attractive destinations for companies seeking environmentally responsible practices.
Features of Green Cities
To achieve their goals, green cities incorporate several key features and practices into their urban planning and development:
Sustainable Transportation
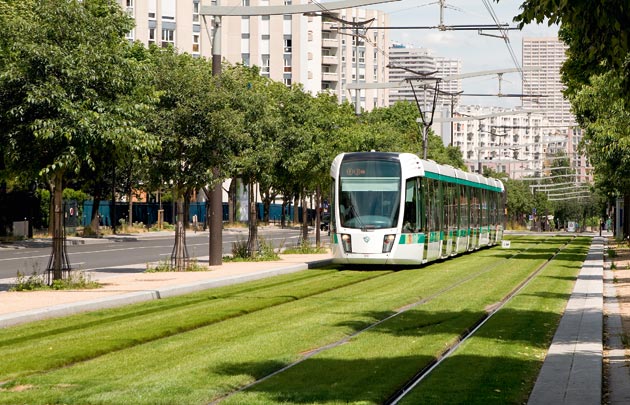

Green cities prioritize sustainable transportation options to reduce reliance on private vehicles. They invest in efficient public transit systems, including buses, trams, and trains, and create pedestrian-friendly infrastructure with well-designed sidewalks and bike lanes. Promoting active transportation not only reduces emissions but also improves public health and quality of life.
Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure refers to the integration of natural elements into the urban environment. This includes the creation of parks, green roofs, vertical gardens, and urban forests. These green spaces enhance biodiversity, mitigate the heat island effect, provide recreational areas for residents, and contribute to cleaner air and water.
Energy-Efficient Buildings
Green cities promote the construction of energy-efficient buildings that minimize energy consumption and reduce carbon footprints. This includes using sustainable materials, implementing efficient insulation, adopting renewable energy sources, and employing smart technologies for energy management. Green buildings help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, decrease energy costs, and create healthier indoor environments for occupants.
Waste Management
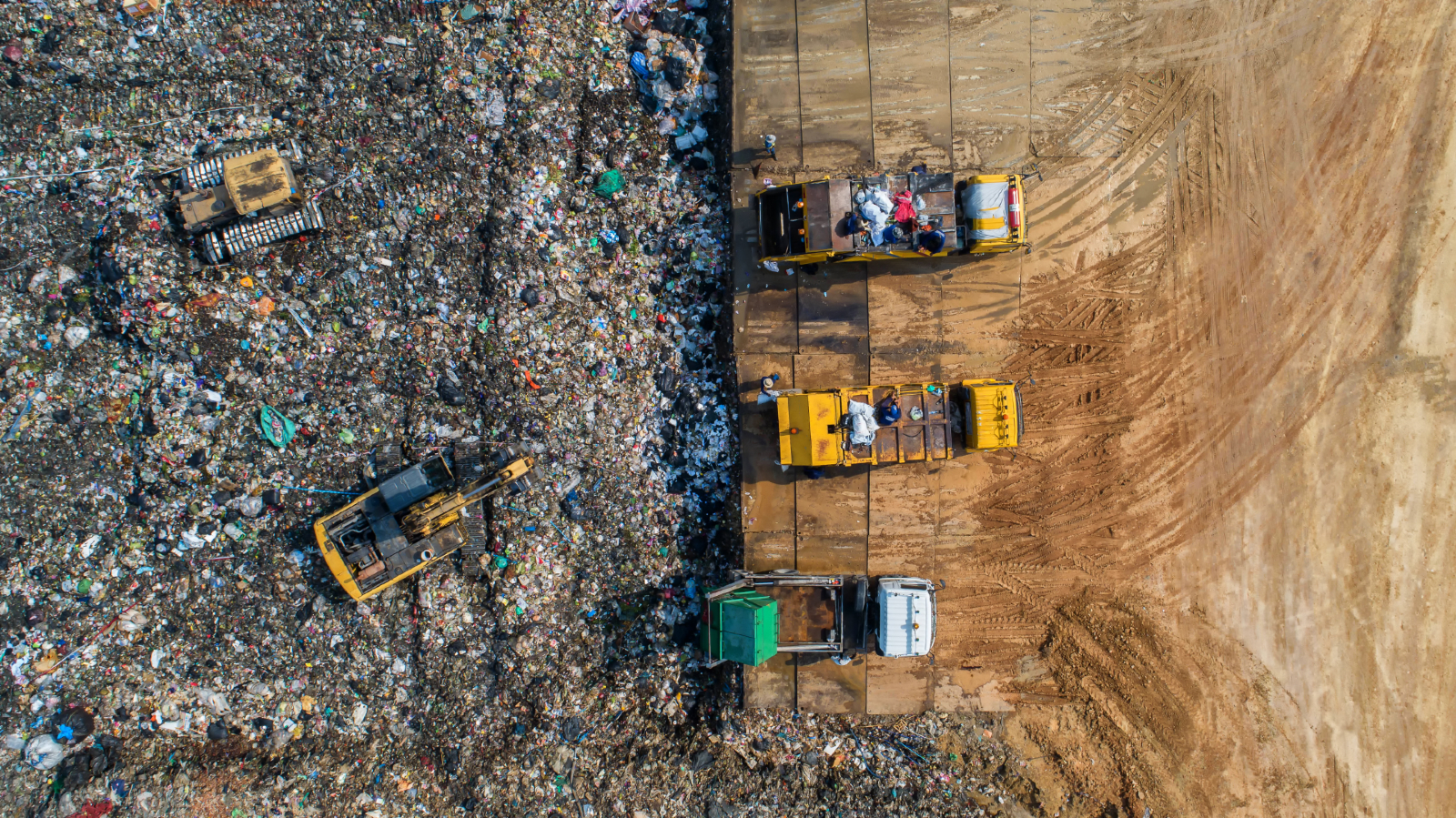

Effective waste management systems are crucial for green cities. These cities implement recycling programs, encourage waste reduction and reuse, and promote composting. Advanced waste-to-energy technologies are also employed to convert organic waste into renewable energy sources, further reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Examples of Green Cities
Several cities around the world serve as prime examples of successful green city initiatives:
Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen is renowned for its commitment to sustainability and cycling culture. The city has invested in an extensive network of bike lanes, making cycling the preferred mode of transportation for many residents. It also has a comprehensive waste management system that emphasizes recycling and energy recovery from waste.
Curitiba, Brazil
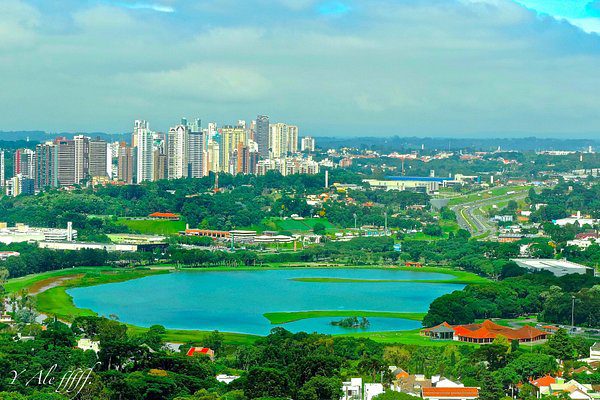

Curitiba is known for its innovative urban planning strategies. The city has implemented a Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) system, reducing traffic congestion and promoting efficient public transportation. Curitiba’s expansive park system and green spaces contribute to its high quality of life and ecological balance.
Vancouver, Canada
Vancouver prioritizes environmental preservation and sustainable practices. The city has set ambitious targets to become the greenest city in the world by 2020. It promotes the use of renewable energy, encourages green building practices, and invests in walkable neighborhoods with ample green spaces.
Singapore
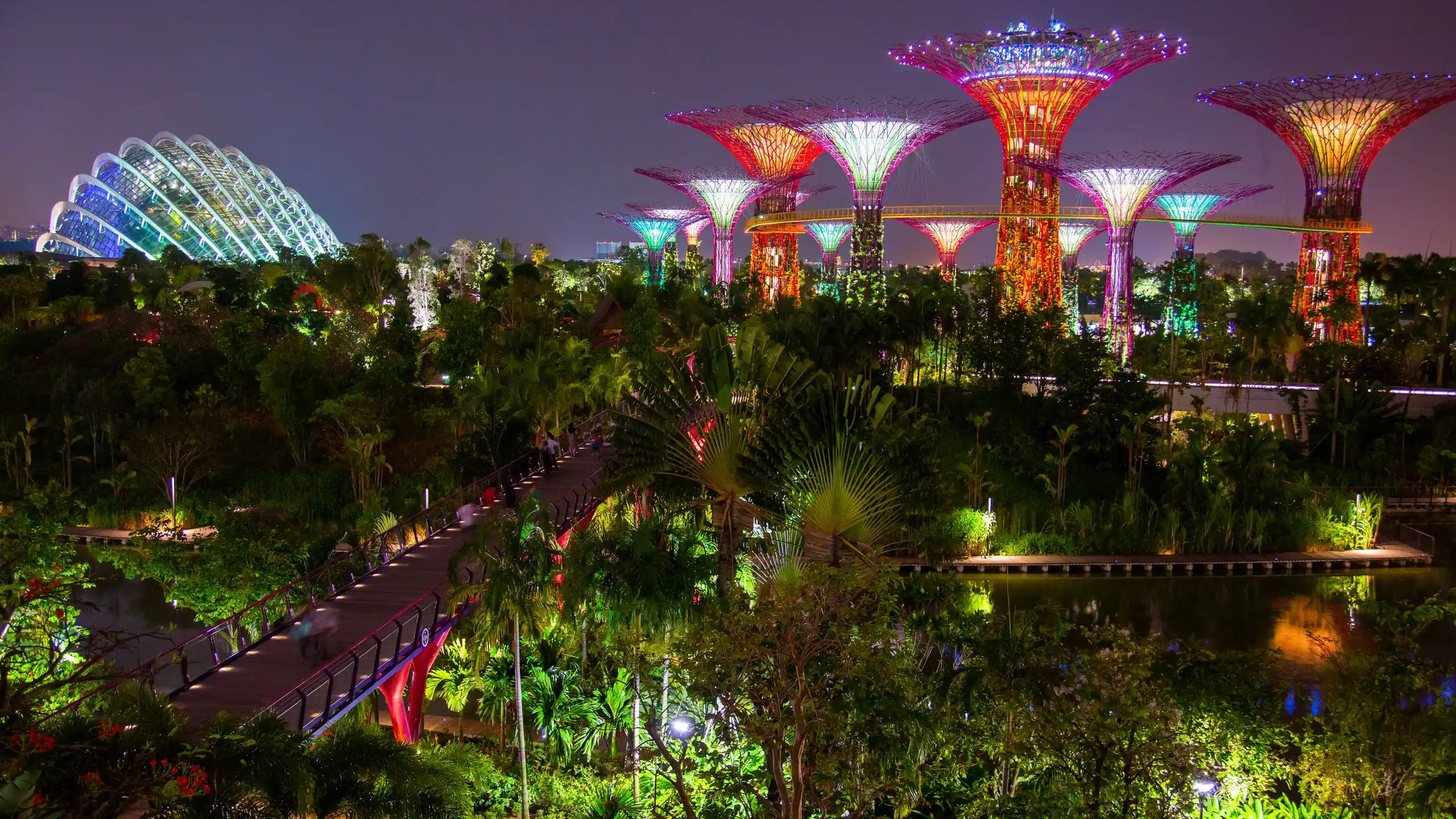

Singapore has emerged as a leader in green urban development despite limited land resources. The city-state has implemented vertical gardens, extensive green roofs, and innovative wastewater management systems. It also actively promotes sustainability education and research to inspire future generations.
Challenges and Solutions in Building Green Cities
While the concept of green cities holds immense promise, there are challenges that need to be overcome to realize their full potential:
Urban Planning and Design
Creating green cities requires thoughtful urban planning and design that prioritizes sustainability and considers the needs of residents. This includes proper zoning, mixed land-use developments, and the integration of green spaces. Collaborative efforts between urban planners, architects, and communities are essential to strike a balance between environmental considerations and livability.
Community Involvement
Engaging the community in the development and maintenance of green cities is crucial for their success. Community participation fosters a sense of ownership and encourages residents to adopt sustainable practices. This can be achieved through education campaigns, participatory design processes, and community gardens where residents can actively contribute to greening efforts.
Financing and Investment
Building green cities often requires significant financial investment. Funding sustainable infrastructure projects and incentivizing private sector participation can be challenging. Governments and stakeholders need to explore innovative financing models, such as public-private partnerships and green bonds, to attract capital and accelerate the transition to green cities.
The Role of Technology in Green Cities
Technology plays a vital role in shaping green cities and enabling their sustainability goals:
Smart Grids
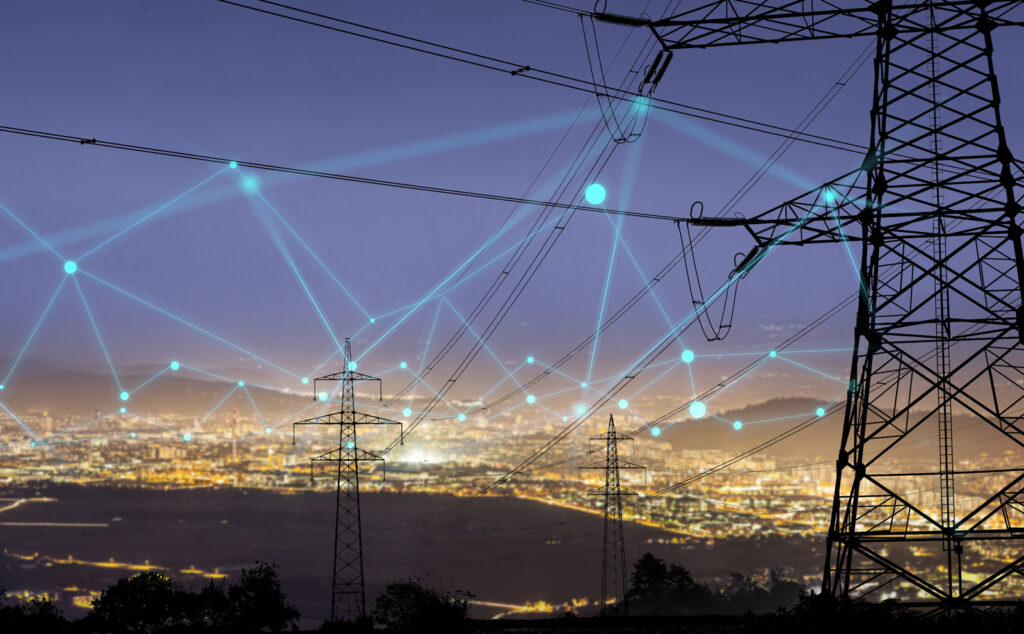

Smart grids incorporate advanced digital technologies to optimize energy distribution, monitor consumption, and manage renewable energy sources. By enhancing the efficiency of the power grid, smart grids support the integration of renewable energy and enable better energy management in green cities.
IoT Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) devices provide real-time data and enable connectivity among various systems and infrastructures within green cities. These devices can monitor energy consumption, air quality, waste management, and other essential factors. By collecting and analyzing data, cities can make informed decisions and implement targeted strategies for sustainability.
Renewable Energy Solutions
Green cities leverage renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. Implementing solar panels on buildings, installing wind turbines, and utilizing geothermal energy contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix.
Conclusion
Green cities represent the future of urban development, offering solutions to the environmental, social, and economic challenges faced by modern societies. By prioritizing sustainability, green cities create livable and vibrant urban environments that benefit both current and future generations. Through sustainable transportation, green infrastructure, energy-efficient buildings, and innovative waste management, these cities serve as beacons of hope for a more sustainable and equitable future. Embracing technology and engaging communities is crucial for the successful implementation of green city initiatives worldwide.
FAQs
1. Are green cities only beneficial for the environment?
Green cities offer a wide range of benefits beyond the environment. They also improve public health, enhance the quality of life for residents, and drive economic growth through sustainable practices.
2. Can existing cities transition to become green cities?
Yes, existing cities can transition towards becoming greener by implementing sustainable policies, investing in renewable energy, enhancing public transportation, and adopting green building practices.
3. How can individuals contribute to creating green cities?
Individuals can contribute by adopting eco-friendly habits, using public transportation or cycling, reducing waste, conserving energy, and participating in community initiatives focused on sustainability.
4. How can technology help in building green cities?
Technology plays a crucial role in green cities by enabling efficient energy management, real-time monitoring of resources, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
5. Are there any challenges in building green cities?
Yes, building green cities comes with challenges such as urban planning, community involvement, and securing adequate financing. However, these challenges can be overcome through collaborative efforts and innovative solutions.