What are Free Radicals and How Do They Affect Our Health?

The Science Behind Free Radicals
Free radicals are a natural byproduct of various metabolic processes in the body, such as the conversion of food into energy. They are also generated when the body is exposed to external factors like pollution, cigarette smoke, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
These unstable molecules can target and damage different types of molecules in the body, including:
- Lipids (fats): Free radicals can cause lipid peroxidation, leading to the breakdown of cell membranes and the release of harmful substances.
- Proteins: Free radicals can alter the structure and function of proteins, impairing their ability to perform their intended roles.
- DNA: Free radicals can damage the genetic material within cells, potentially leading to mutations and increased risk of cancer.
The body’s natural defense mechanisms, such as antioxidants, work to neutralize free radicals and prevent them from causing extensive damage. However, when the production of free radicals exceeds the body’s ability to neutralize them, a state of oxidative stress can occur, leading to a range of health issues.
Sources of Free Radicals in Our Environment
Free radicals can come from both internal and external sources. Understanding the various sources of free radicals is crucial in minimizing your exposure and taking proactive steps to protect your health.
Internal sources of free radicals include:
- Normal metabolic processes, such as cellular respiration and inflammation
- Immune system responses to pathogens and infections
External sources of free radicals include:
- Air pollution, including vehicle emissions and industrial pollutants
- Cigarette smoke and secondhand smoke
- Exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds
- Certain medications and medical treatments, such as chemotherapy
- Consumption of processed and fried foods
- Exposure to pesticides and other chemicals
By recognizing these sources, you can make informed decisions to reduce your exposure and take steps to mitigate the impact of free radicals on your health.
The Impact of Free Radicals on Our Health
Free radicals can have a profound impact on our overall health, contributing to the development and progression of various chronic diseases. Understanding the connection between free radicals and specific health conditions is essential in taking proactive measures to protect your well-being.
Common Health Conditions Associated
- Cardiovascular disease: Free radicals can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Cancer: Free radicals can damage DNA, leading to genetic mutations and the potential development of cancerous cells.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Free radicals have been linked to the progression of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.
- Diabetes: Oxidative stress caused by free radicals can impair insulin sensitivity and contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Chronic inflammation: Free radicals can trigger and perpetuate inflammatory responses, leading to conditions like arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and chronic pain.
- Premature aging: Free radicals can accelerate the aging process, contributing to the development of wrinkles, age spots, and other signs of premature aging.
Antioxidants and Their Role in Combating Free Radicals
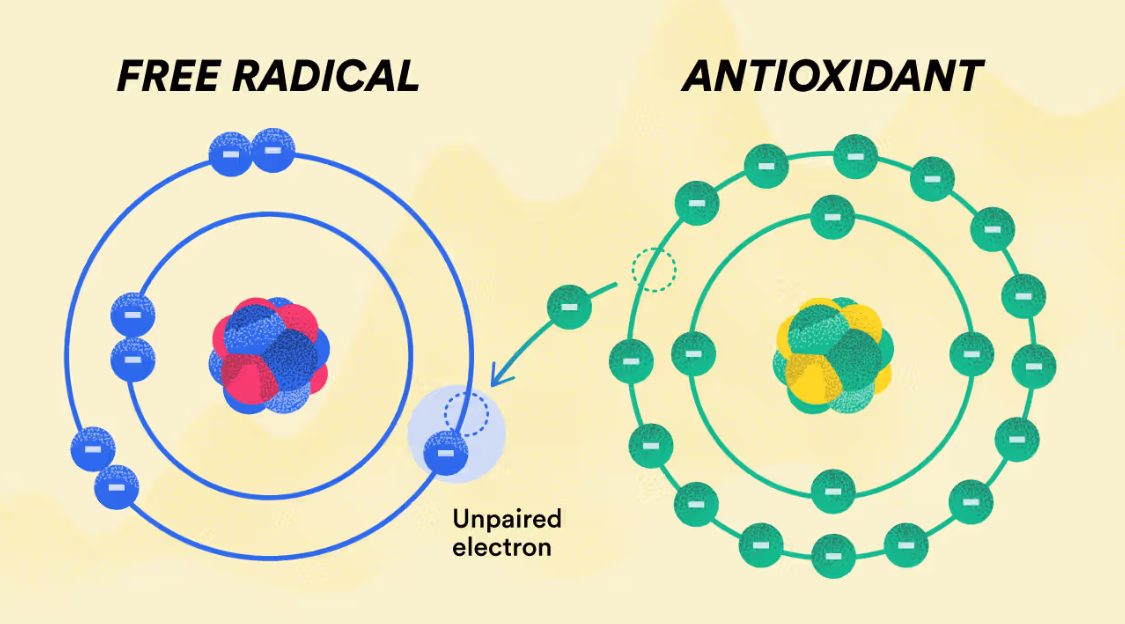
Antioxidants are substances that can neutralize free radicals and prevent them from causing cellular damage. They work by donating an electron to the free radical, stabilizing it and preventing it from causing further harm.
There are two main types of antioxidants:
- Endogenous antioxidants: These are produced naturally by the body and include enzymes like superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase.
- Exogenous antioxidants: These are obtained from external sources, such as the foods we eat and supplements we take. Examples include vitamins C and E, carotenoids, and polyphenols.
By incorporating antioxidant-rich foods and supplements into your diet, you can help support your body’s natural defenses against free radicals and reduce the risk of developing various health conditions.
How to Reduce Exposure to Free Radicals
Minimizing your exposure to free radicals is an essential step in maintaining good health. Here are some strategies you can implement:
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Engage in regular exercise, get enough sleep, and manage stress levels, as these factors can help reduce the production of free radicals in the body.
- Avoid environmental toxins: Limit your exposure to air pollution, cigarette smoke, and other sources of environmental toxins that can contribute to free radical formation.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation: Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or tanning beds.
- Choose a balanced diet: Incorporate a variety of antioxidant-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, into your daily meals.
- Consider antioxidant supplements: If your dietary intake of antioxidants is insufficient, you may want to consult with a healthcare professional about taking antioxidant supplements to support your body’s defenses.
Incorporating Antioxidant-Rich Foods into Your Diet
Incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into your diet is a simple and effective way to combat the harmful effects of free radicals. Here are some examples of nutrient-dense, antioxidant-packed foods to include in your meals:
- Berries (blueberries, raspberries, blackberries, and strawberries)
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and collard greens)
- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds)
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, and sardines)
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat)
- Spices (turmeric, ginger, and cinnamon)
Incorporating a variety of these antioxidant-rich foods into your daily diet can help neutralize free radicals and support your overall health.
The Importance of a Balanced Lifestyle
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle is crucial in minimizing the damaging effects of free radicals. In addition to incorporating antioxidant-rich foods and reducing environmental exposures, consider the following lifestyle factors:
- Stress management: Chronic stress can increase the production of free radicals, so it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through meditation, yoga, or other relaxation techniques.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can help boost the body’s natural antioxidant defenses and reduce inflammation, which can contribute to free radical damage.
- Adequate sleep: Lack of sleep can lead to increased oxidative stress, so aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out toxins and support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
- Avoidance alcohol consumption: Alcohol intake can increase the production of free radicals and contribute to oxidative stress.
By adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses multiple aspects of your lifestyle, you can effectively minimize the impact of free radicals and support your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health by Understanding and Addressing Free Radicals
Free radicals play a significant role in the development of various chronic health conditions, from cardiovascular disease to cancer. By understanding the science behind free radicals, recognizing their sources, and implementing strategies to combat their harmful effects, you can take control of your health and reduce your risk of these debilitating conditions.
Start your journey to better health today by incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into your diet and adopting a balanced lifestyle that supports your body’s natural defenses against free radicals. Remember, small changes can make a big impact on your overall well-being.