
In recent years, the rising concerns about climate change and the need for sustainable transportation have led to a surge in the popularity of electric cars. Electric cars, also known as electric vehicles (EVs), are vehicles powered by one or more electric motors, using electricity stored in rechargeable batteries instead of traditional fossil fuels like gasoline or diesel.
What are Electric Cars?
Electric cars are automobiles that use electricity as their primary source of power. They have electric motors that drive the wheels, powered by rechargeable batteries. Unlike conventional vehicles that rely on internal combustion engines, electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them an eco-friendly alternative.
Benefits of Electric Cars
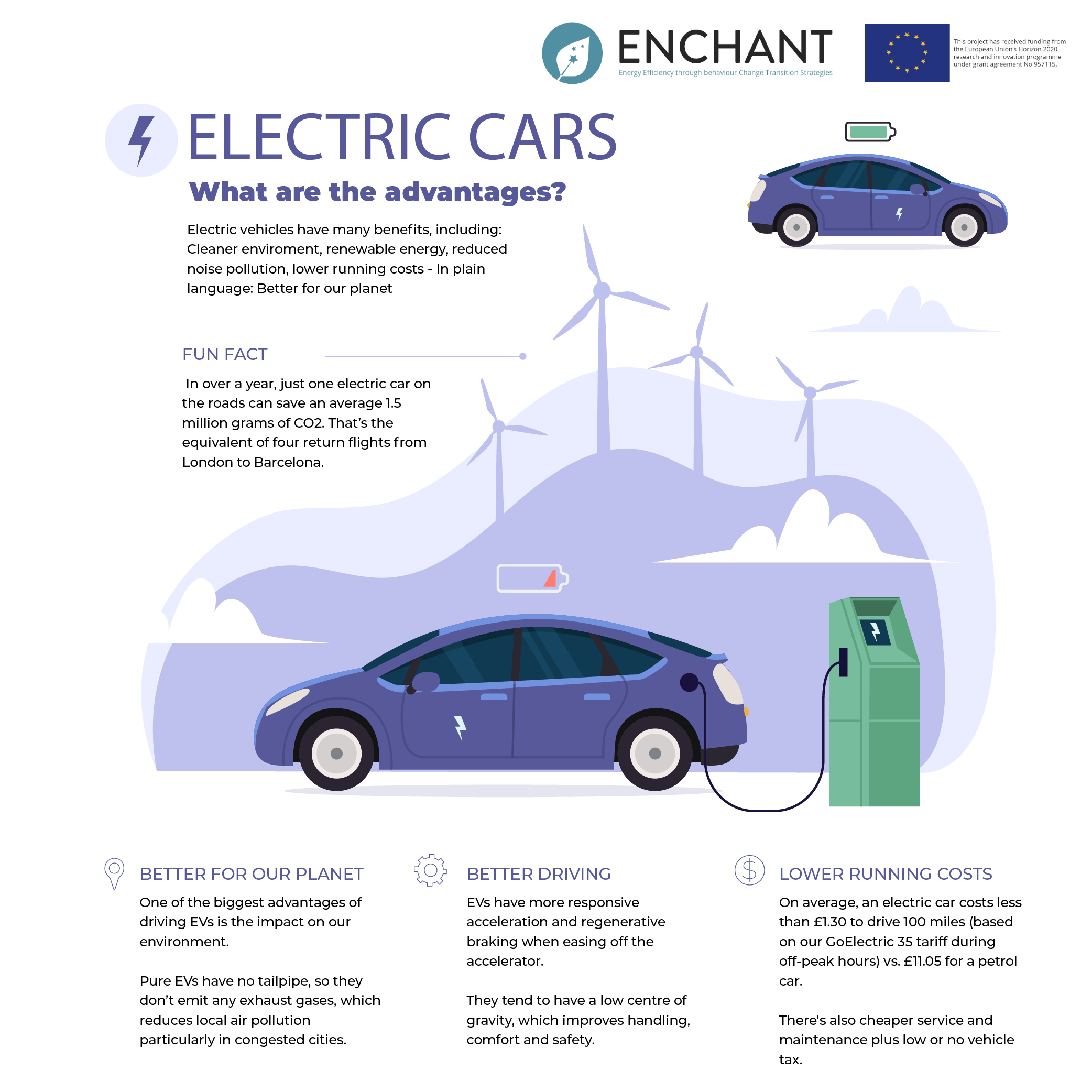
Electric cars offer numerous benefits that make them an attractive choice for environmentally conscious consumers. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
Environmental Impact
One of the most significant advantages of electric cars is their positive impact on the environment. By eliminating tailpipe emissions, electric cars contribute to cleaner air and help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This leads to improved air quality, reduced pollution-related health issues, and a smaller carbon footprint.
Cost Savings
While the upfront cost of electric cars may be higher than traditional vehicles, they offer long-term cost savings. Electric cars have lower maintenance and fuel costs compared to internal combustion engine vehicles. Charging an electric car is generally cheaper than filling up a gasoline tank, and the reduced need for regular maintenance, such as oil changes, contributes to additional savings over time.
Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels
Electric cars provide an opportunity to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. With renewable energy sources like solar and wind power becoming more accessible, the electricity used to charge electric cars can be generated sustainably. This shift away from fossil fuels has the potential to decrease our reliance on foreign oil and create a more resilient energy infrastructure.
Quieter and Smoother Driving Experience
Electric cars provide a quieter and smoother driving experience compared to traditional vehicles. The electric motors generate minimal noise, resulting in a quieter cabin environment and reduced noise pollution in urban areas. Electric cars also offer instant torque, providing quick acceleration and a smooth driving experience. The absence of gear shifting and the smooth power delivery contribute to a comfortable and enjoyable ride.
How do Electric Cars Work?
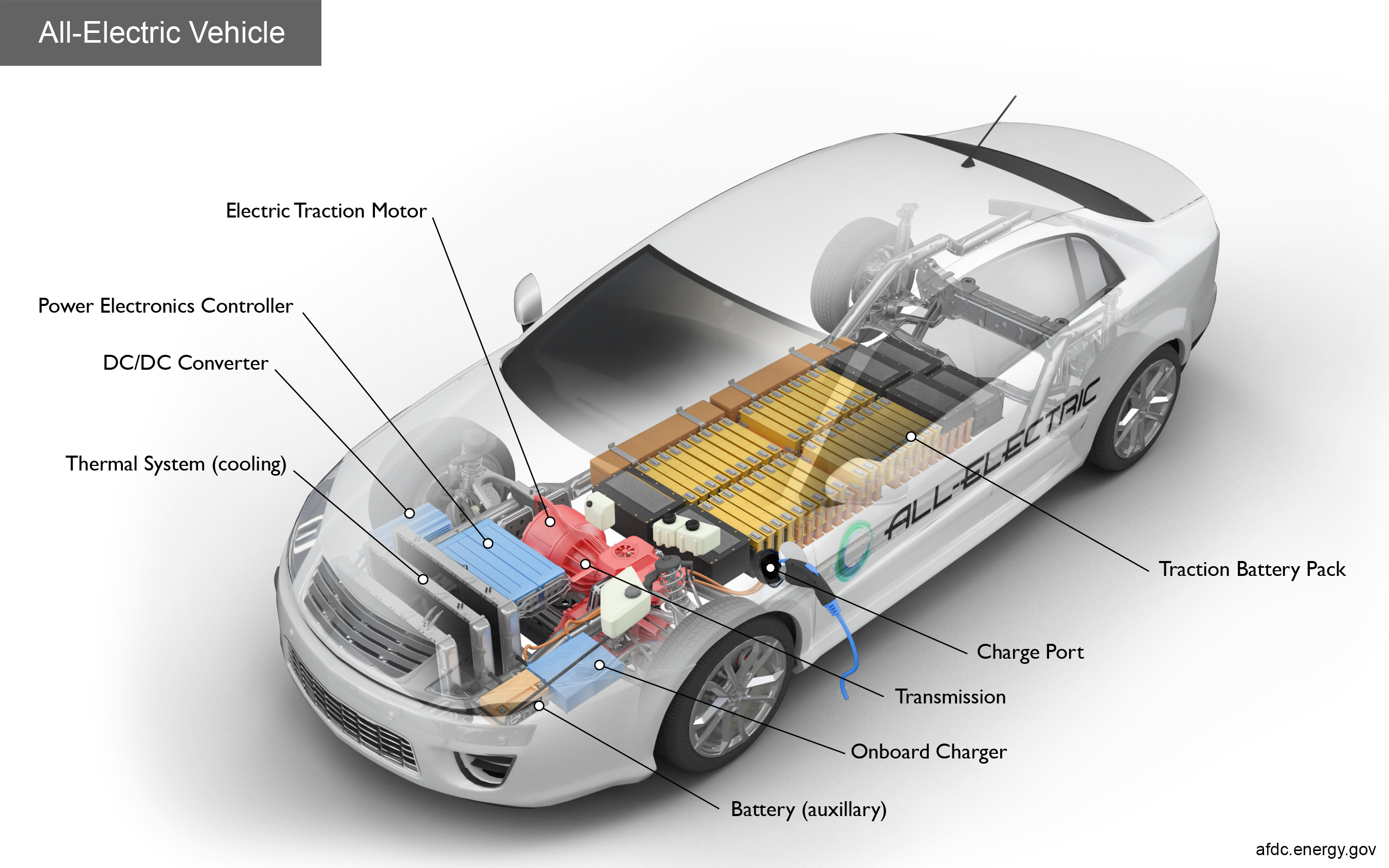
Electric cars operate by converting electrical energy stored in the batteries into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle. The electric motor delivers power to the wheels, providing instant torque and smooth acceleration. The batteries are recharged by plugging the car into an external power source, such as a charging station or a wall outlet.
Types of Electric Cars
There are different types of electric cars available in the market, each with its unique characteristics and capabilities. Let’s take a closer look at the three main types:
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
Battery Electric Vehicles, or BEVs, are fully electric cars that rely solely on battery power. They do not have a combustion engine and must be charged using an external power source. BEVs offer zero tailpipe emissions and have the longest driving range among electric cars.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)

Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles, or PHEVs, combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine. PHEVs can run on electricity alone for shorter distances, and when the battery is depleted, they switch to using gasoline or diesel. This hybrid design provides flexibility and helps alleviate range anxiety.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles, or FCEVs, use hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air to generate electricity through a chemical reaction. FCEVs produce zero emissions and offer longer driving ranges compared to traditional battery-powered electric cars. However, the availability of hydrogen refueling infrastructure is currently limited.
Charging Infrastructure
A robust charging infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric cars. Let’s explore the different charging options available:
Home Charging
Home charging is the most convenient and common way to charge electric cars. By installing a charging station at home, owners can easily charge their vehicles overnight or whenever they are parked at home. This ensures a fully charged car every morning and eliminates the need for frequent public charging.
Public Charging Stations
Public charging stations are essential for longer trips or when home charging is not feasible. They can be found in various locations such as shopping centers, parking lots, and highways. Public charging stations offer different charging speeds, ranging from regular charging to fast charging, allowing electric car owners to recharge their vehicles while on the go.
Fast Charging

Fast charging, also known as rapid charging or DC fast charging, provides a significant amount of power to quickly charge an electric car’s battery. Fast charging stations are capable of delivering high voltage and high current, allowing drivers to charge their vehicles to 80% capacity in a short amount of time.
Factors Affecting Range
Several factors can affect the range of an electric car. Driving at higher speeds, using heating or air conditioning, and driving on hilly terrain can decrease the range. Cold weather also reduces battery efficiency, resulting in a shorter range. On the other hand, driving at lower speeds, utilizing regenerative braking, and maintaining proper tire pressure can help maximize the range.
Range Anxiety and Battery Technology
Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery charge during a journey, has been a concern for many potential electric car buyers. However, advancements in battery technology have significantly improved the range and charging times of electric cars. Modern electric cars can travel hundreds of miles on a single charge, and fast charging options have reduced the time required for recharging.
Electric Cars and the Future
The future of transportation is undoubtedly electric. Governments around the world are implementing initiatives to encourage the adoption of electric cars. Technological advancements, such as more efficient batteries and improved charging infrastructure, are further driving the growth of electric vehicles.
Top 10 Electric Cars For This Year

When it comes to the top 10 electric cars available in the market, there are several impressive options to choose from. These electric vehicles combine sustainability, performance, and advanced technology to provide an exceptional driving experience. From the luxurious Tesla Model S and Audi e-tron to the practical Nissan Leaf and Chevrolet Bolt EV, each car offers its unique features and benefits. Whether you’re looking for a high-performance sedan or a spacious SUV, the top 10 electric cars provide a range of options to suit different preferences and needs.
Government Incentives and Support
Governments around the world are implementing various incentives and policies to encourage the adoption of electric cars. These initiatives aim to accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Subsidies and Tax Credits
Many countries offer subsidies and tax credits to reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an electric car. These incentives can significantly lower the price gap between electric cars and conventional vehicles. Additionally, some governments provide incentives for installing home charging stations, making it more affordable for individuals to charge their electric cars at home.
Infrastructure Development
To support the growth of the electric car market, governments are investing in the development of charging infrastructure. This includes expanding the network of public charging stations, installing fast-charging stations along major highways, and promoting the integration of charging infrastructure in residential areas and workplaces. The goal is to make charging convenient and accessible for electric car owners, regardless of their location.
Emission Regulations
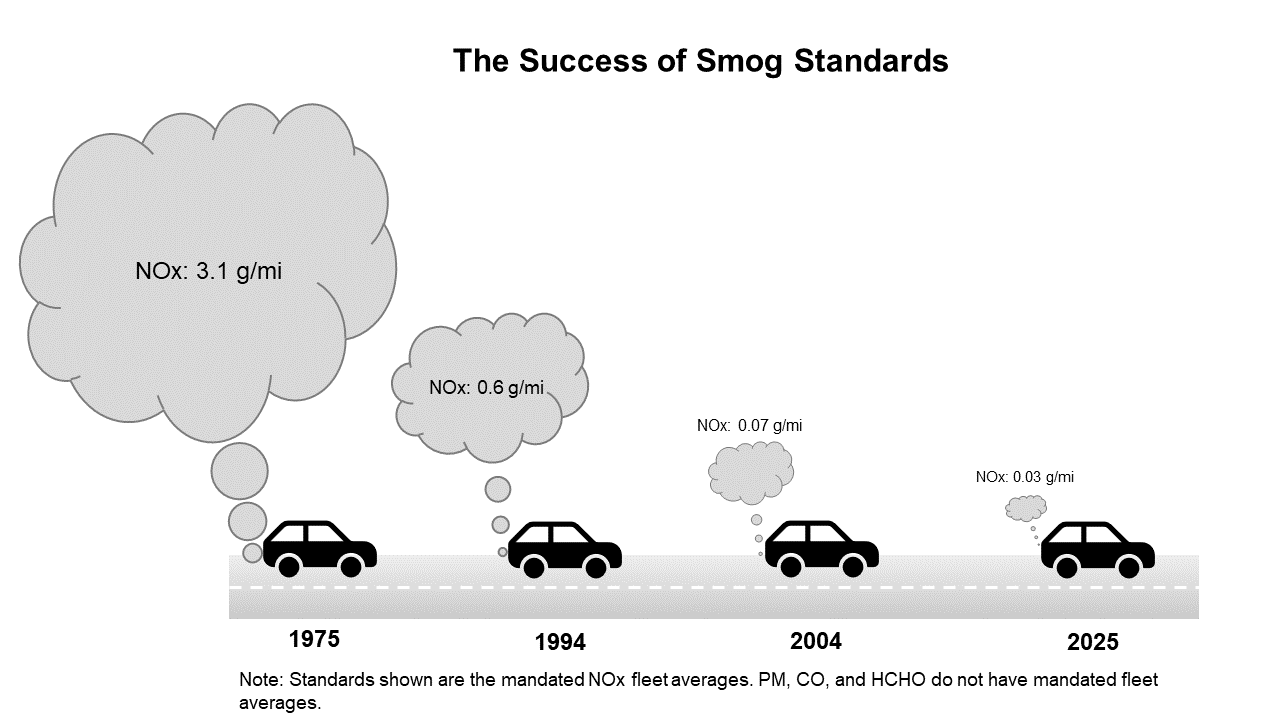
To reduce air pollution and combat climate change, governments are implementing stricter emission regulations. These regulations aim to encourage automakers to produce more electric cars and phase out the production of vehicles with internal combustion engines. By setting emission standards and promoting zero-emission vehicles, governments are creating a favorable environment for the growth of the electric car industry.
Challenges and Limitations
While electric cars offer numerous benefits, there are still some challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for wider adoption.
Limited Charging Infrastructure
Although the charging infrastructure is continually improving, there is still a need for further expansion and standardization. The availability of charging stations, especially in rural areas or certain regions, can be limited. Ensuring a robust and reliable charging network is crucial for electric car owners to have the confidence to travel long distances and rely on their vehicles for daily commuting.
Higher Upfront Costs
Electric cars generally have a higher upfront cost compared to conventional vehicles. This is primarily due to the expensive battery technology and limited economies of scale in production. However, as technology advances and production volumes increase, the cost of electric cars is expected to decrease, making them more affordable for a wider range of consumers.
Range Limitations

While the range of electric cars has improved significantly in recent years, there is still a perception that they cannot match the range of traditional vehicles. Although electric cars can typically cover the daily commuting needs of most individuals, long-distance travel may require careful planning and utilization of fast-charging networks. Continued advancements in battery technology and the expansion of charging infrastructure will further alleviate range limitations.
Recycling and Disposal of Batteries
As the number of electric cars increases, proper recycling and disposal of batteries become crucial to minimize environmental impact. Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in electric cars, contain valuable and potentially hazardous materials. Developing efficient and environmentally friendly battery recycling methods is essential to ensure the sustainability of electric cars.
Future of Electric Cars
The future of electric cars looks promising, with ongoing technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements continue to enhance the performance, range, and charging capabilities of electric cars. Battery technology is expected to improve, resulting in increased energy density and longer ranges. Moreover, research and development efforts are focused on developing solid-state batteries, which offer higher energy density and faster charging times. Other advancements include lightweight materials, improved aerodynamics, and smart connectivity features that enhance the overall efficiency and driving experience of electric cars.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Electric cars can play a significant role in the integration of renewable energy sources into the electricity grid. By charging during periods of excess renewable energy generation, such as during the day when solar power is abundant, electric cars can serve as energy storage devices. This helps balance the electricity grid and maximizes the utilization of renewable energy resources. Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology enables electric cars to discharge power back to the grid when needed, providing a decentralized and flexible energy storage solution.
Autonomous Driving and Connectivity
The future of electric cars goes beyond their power source. The integration of autonomous driving technology and advanced connectivity features will revolutionize transportation. Electric cars are well-suited for autonomous driving due to the simplicity and precision of electric drivetrains. Additionally, electric cars can be seamlessly connected to smart cities and infrastructure, enabling efficient traffic management, optimized routing, and enhanced overall transportation experience.
Conclusion
Electric cars have emerged as a sustainable and efficient alternative to conventional vehicles. With their environmental benefits, cost savings, and technological advancements, electric cars are reshaping the automotive industry. While challenges such as charging infrastructure and range limitations exist, ongoing efforts from governments, automakers, and technology companies are paving the way for a future where electric cars dominate the roads. As the industry continues to evolve, electric cars will play a crucial role in achieving a greener and more sustainable transportation system.
FAQs
1. Are electric cars more expensive to maintain?
Electric cars generally have lower maintenance costs compared to conventional vehicles. They have fewer moving parts, no oil changes, and reduced wear on components like brakes. However, battery-related maintenance and eventual replacement may incur additional costs.
2. How long does it take to charge an electric car?
The charging time depends on the type of charger used and the electric car's battery capacity. Level 1 charging can take several hours, while Level 2 charging can provide a full charge in a few hours. Fast-charging stations can charge the battery to 80% or more in around 30 minutes.
3. Can I charge an electric car at home?
Yes, you can charge an electric car at home by installing a home charging station. Home charging provides convenience and allows for overnight charging, ensuring a full battery in the morning.
4. What is range anxiety?
Range anxiety refers to the fear or concern of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station. As charging infrastructure improves and electric cars offer longer ranges, range anxiety is gradually diminishing.
5. How eco-friendly are electric cars?
Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. However, the environmental impact depends on the source of electricity used for charging. Charging with renewable energy sources further enhances the eco-friendliness of electric cars.





