
One of the biggest advantages of electric cars is their positive impact on the environment. Unlike traditional gasoline-powered cars, electric cars do not emit harmful pollutants into the air. This means that electric cars contribute significantly less to air pollution, which is a leading cause of respiratory illnesses and other health problems.

Furthermore, electric cars do not release greenhouse gases, which contribute to climate change. By using renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power to charge electric cars, their carbon footprint can be reduced to almost zero. This means that electric cars are an important part of the solution to reducing the effects of climate change.
Cost Savings of Electric Cars
Another major advantage of electric cars is the cost savings they offer. While electric cars may have a higher upfront cost than traditional gasoline-powered cars, they are much cheaper to maintain and operate in the long run. For example, electric cars require less maintenance since they have fewer moving parts and do not require oil changes. Additionally, they are much cheaper to fuel since electricity is less expensive than gasoline.
Furthermore, many governments offer incentives such as tax credits or rebates to promote the use of electric cars. In some states in the US, for example, electric car owners can receive up to $7,500 in federal tax credits. This can significantly reduce the overall cost of purchasing an electric car.
The Future of Electric Cars

The future of electric cars is bright. Many major car manufacturers are investing heavily in electric car technology, which means that we can expect to see more electric car models on the market in the coming years. Additionally, with advancements in battery technology, electric cars are becoming more efficient and have longer ranges.
Another exciting development is the potential for electric cars to be used in conjunction with renewable energy sources such as solar panels. By using solar power to charge electric cars, we can create a completely sustainable and eco-friendly mode of transportation.
Misconceptions about Electric Cars
Despite the many benefits of electric cars, there are still some misconceptions about them. One common myth is that electric cars have a short range. While this may have been true in the past, many modern electric cars have ranges of over 200 miles on a single charge. This means that electric cars can be used for long-distance travel just like traditional cars.
Another myth is that electric cars are not as powerful as gasoline-powered cars. While it’s true that electric cars may not have the same top speed as some high-performance gasoline cars, electric cars have instant torque, which means that they can accelerate quickly and smoothly.
Government Incentives for Electric Cars
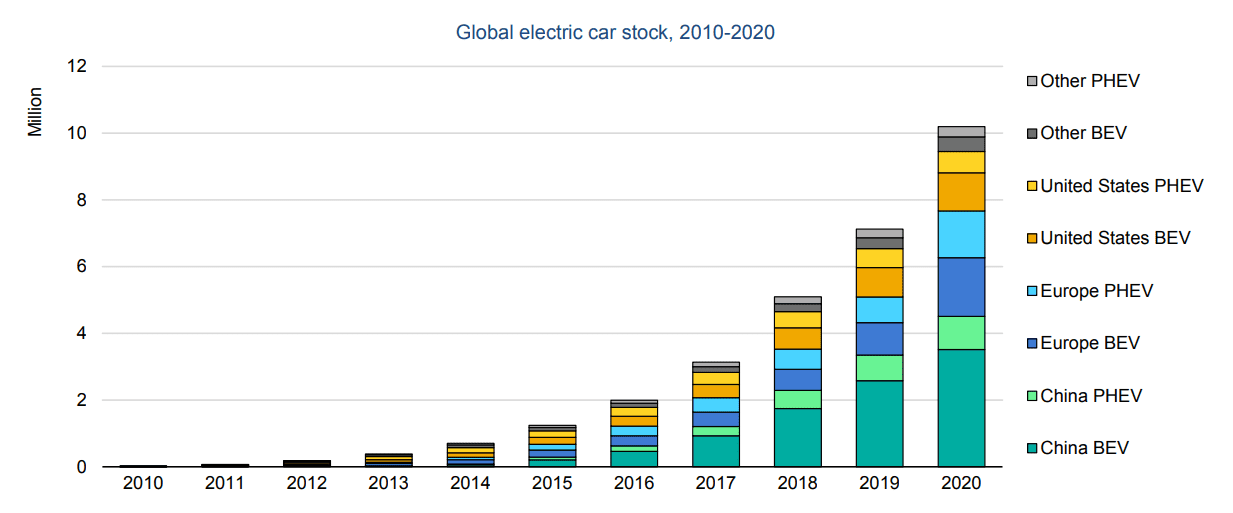
To encourage the adoption of electric cars, many governments offer incentives for purchasing and using them. In addition to tax credits and rebates, some governments offer free parking or tolls for electric car owners. Additionally, some cities have designated electric car-only lanes to ease traffic congestion and reduce emissions.
The Most Popular Electric Car Models
There are many electric car models available on the market, but some have become more popular than others. The Tesla Model 3, for example, is one of the most popular electric cars due to its long-range and sleek design. Other popular electric car models include the Nissan Leaf, the Chevrolet Bolt, and the BMW i3.
Charging Infrastructure for Electric Cars
As the number of electric cars on the road continues to grow, so does the need for charging infrastructure. Fortunately, many governments and private companies are investing in building more charging stations. In the US, for example, there are over 25,000 public charging stations and that number is growing every year.
Additionally, many electric car owners charge their cars at home using a charging station. This is convenient since the car can be charged overnight while the owner is sleeping.
Maintenance and Repair of Electric Cars

Electric cars require less maintenance than traditional cars since they have fewer moving parts. However, it’s still important to keep the car in good condition to ensure that it runs efficiently. Regular maintenance such as tire rotations and brake checks should still be performed.
Additionally, it’s important to find a mechanic who is trained to work on electric cars. Since electric cars are still a relatively new technology, not all mechanics are familiar with how to repair them.
Conclusion: The Impact of Electric Cars on the Environment and Society
Electric cars have the potential to revolutionize the way we think about transportation. By reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing harmful emissions, electric cars can have a positive impact on the environment and our health. Additionally, electric cars offer cost savings
Electric Cars FAQs
Q: What are the 4 types of electric cars?
A: The four types of electric cars are as follows:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): These cars are solely powered by an electric motor and rely on a rechargeable battery pack for energy. They do not have a combustion engine and produce zero emissions.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): These cars combine an electric motor with a traditional internal combustion engine. They have a larger battery pack compared to regular hybrid cars and can be charged from an external power source.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): HEVs use both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine to power the vehicle. The electric motor assists the engine during acceleration and captures energy through regenerative braking.
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): FCEVs use hydrogen gas to generate electricity through a chemical reaction in a fuel cell. The electricity produced powers the electric motor, with water vapor being the only emission.
Q: What are the 3 disadvantages of an electric car?
A: While electric cars have numerous advantages, they also come with a few disadvantages:
- Limited driving range: Electric cars typically have a limited range on a single charge compared to conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. Although the range is improving with advancements in battery technology, long-distance travel may still require careful planning.
- Charging infrastructure: The availability of charging stations can be a concern, especially in certain areas or regions with limited infrastructure. Charging an electric car takes longer than refueling a gasoline car, so access to convenient and reliable charging points is important.
- Upfront cost: Electric cars often have a higher upfront cost compared to their gasoline counterparts. This is mainly due to the cost of battery technology, which is gradually decreasing but still contributes to the initial price difference. However, lower operating costs and potential incentives can offset this disadvantage over time.
Q: How does an electric car work?
A: Electric cars use an electric motor powered by a rechargeable battery pack to propel the vehicle. When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, electricity from the battery is sent to the motor, which generates rotational energy. This energy is then transferred to the wheels, propelling the car forward.
The battery pack of an electric car can be recharged by plugging it into an external power source, such as a charging station or a regular electrical outlet. Electric cars also utilize regenerative braking, which converts kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration, helping to recharge the battery.
Q: What are the benefits of an electric car?
A: Electric cars offer several benefits, including:
- Environmental friendliness: Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. They contribute to improving air quality and combating climate change when powered by renewable energy sources.
- Energy efficiency: Electric motors are more efficient than internal combustion engines, converting a higher percentage of energy from the battery to power the vehicle. This efficiency translates into lower energy consumption and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
- Lower operating costs: Electric cars have lower operating costs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, and electric cars require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes.
- Quiet and smooth driving experience: Electric cars produce minimal noise and vibrations, providing a quieter and smoother driving experience. This can contribute to reduced noise pollution in urban areas.
Q: Why are electric cars good?
A: Electric cars are considered good for several reasons:
- Environmental impact: Electric cars have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels and producing zero tailpipe emissions, they contribute to mitigating climate change and improving air quality.
- Energy diversification: Electric cars promote energy diversification by utilizing electricity from various sources, including renewable energy. This reduces dependence on finite fossil fuel reserves and helps transition to a more sustainable energy mix.
- Technological advancement: The development and adoption of electric cars drive innovation in the automotive industry. It leads to advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and overall energy efficiency, benefiting not only electric vehicles but also other sectors.
- Economic benefits: The growth of the electric vehicle market stimulates economic activity and job creation in various industries, such as manufacturing, renewable energy, and charging infrastructure. It also reduces dependence on imported oil, enhancing energy security for countries.
Overall, electric cars are seen as a positive solution for transportation, aligning with sustainability goals and offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.





